1 题目要求
1.1 背景
随着城市轨道交通的快速发展,地铁已成为现代都市出行的核心方式之一。乘客在出行时,往往需要根据多种因素(如时间、距离、费用)选择最优路径。然而,地铁网络结构复杂,站点间存在多条路径,单一指标无法满足用户多样化需求。因此,开发一个智能的地铁线路规划查询程序,能够为任意两站提供多目标路径推荐,具有重要的实际应用价值。
1.2 目标
开发一个地铁线路规划查询程序,实现以下核心功能:
- 路径查询:允许用户输入任意起始站和终点站,查询所有可行的路径。
- 多目标推荐:根据价格、距离和时间三个指标,计算并推荐多种路径选项。
- 数据集成:构建结构化数据库,支持路径计算。
- 网状规划:将地铁网络建模为图结构,利用算法解决多目标优化问题。
- 用户界面:提供友好的图形界面,方便用户输入查询条件和查看结果。
设计与实现
系统架构
为了使项目具备更好的可维护性和可拓展性,我们采取了模块化设计思想,将系统划分为多个独立的模块,包括数据获取模块、路径计算模块和用户界面模块。各个模块之间通过清晰的接口进行交互,便于后续的功能扩展和维护。
有关于项目的模块划分,请参见下图:
数据获取模块
地铁数据来源于高德地图开放的地铁线路 API,每个城市对应唯一的数据链接。例如,西安的数据接口为:
https://map.amap.com/service/subway?_1759306864569&srhdata=6101_drw_xian.json
然而,原始数据为 JSON 格式,结构较为复杂。项目通过parse_metro_info()函数,将原始数据解析为统一的数据结构:
| |
核心算法模块
路径规划核心模块主要负责根据用户输入的起点和终点,结合当前地铁线路数据,计算出最优的地铁出行方案。该模块实现了多种策略的路线规划算法,并确保结果的准确性与实用性。
模块首先通过解析后的地铁数据,将整个地铁网络抽象为图结构:
- 站点建模:每个地铁站点(
Station类)拥有唯一 ID、名称、所属线路及经纬度坐标。 - 邻接表构建:每个站点与其前后相邻站点通过邻接表连接,形成完整的地铁路网。对于环线,首尾站点相互连接,支持环线路径规划。
为了适应换乘站的情况,我们在Station类中的所属线路属性中,使用列表来存储一个站点可能属于的多个线路信息。每个线路信息由一个StationInLine类表示,包含线路名称、相邻站点等信息。
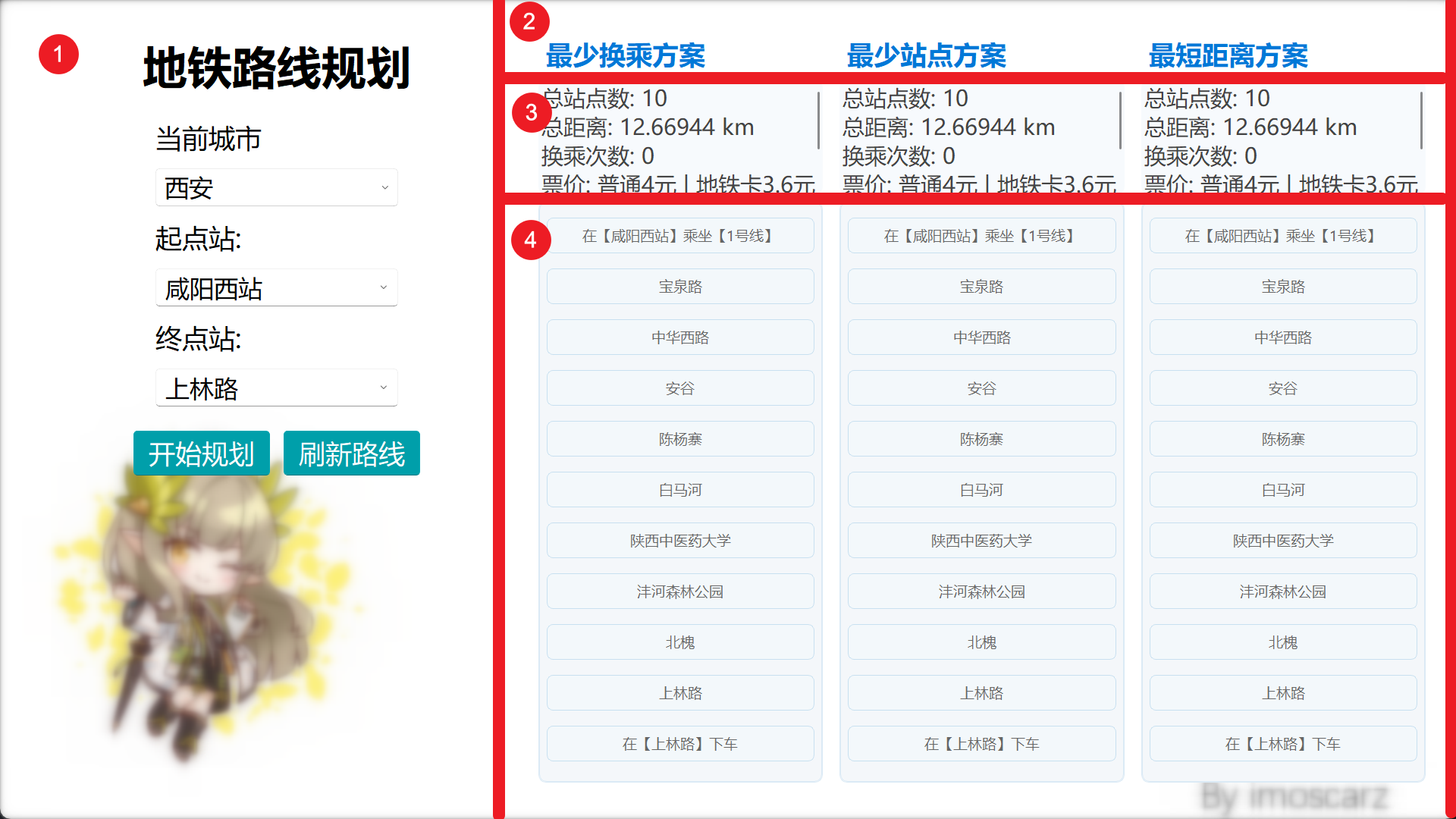
用户界面模块
本项目的 UI 模块采用了 PyQt5 和 qfluentwidgets 库实现。
其他模块
在assets模块中,我们储存了项目所需的静态资产,如背景图片、图标等。
在utils模块中,我们实现了一些通用的工具函数,如票价计算、距离计算,便于其他模块调用。
测试与验证
为了确保系统的稳定性和准确性,我们对各个模块进行了充分的测试。测试主要分为单元测试和集成测试两部分。
单元测试主要针对各个函数和类的功能进行验证,确保其在各种输入下都能返回正确的结果。我们使用了 unittest 框架编写了详细的测试用例,并覆盖了常见的边界情况。
集成测试则关注模块之间的协作,确保数据流和控制流的正确性。我们模拟了用户的实际操作场景,验证了从数据获取到路径规划再到结果展示的整个流程。
封装与打包
我们使用 Nuitka 工具对项目进行封装。Nuitka 将 Python 模块翻译成 C 级程序,然后使用 libpython 和自己的静态 C 文件,以 CPython 的方式执行。这种方法相比于pyinstaller 等工具的简单封装,能够生成更小的可执行文件,并且有着更高的运行效率。
在使用过程中,我们发现 Nuitka 工具在处理 PyQt5 的依赖库 SciPy 时,存在一定的兼容性问题,导致部分功能无法正常使用。为了解决这个问题,我们尝试了多种方案,通过手动指定依赖库的方法,最终成功实现了与 Nuitka 的兼容。
| |
拓展与反思
项目的拓展
由于在项目设计时我们使用了模块化的设计思路,使得各个模块之间的耦合度较低,便于后续的功能扩展和维护。而由于我们通过远程数据接口获取地铁线路和站点信息,未来可以方便地接入更多城市的地铁数据,扩展系统的适用范围。
随着城市地铁数据的不断增加,我们需要对数据获取模块进行重构,以支持更多城市的地铁线路和站点信息。我们计划将数据获取模块设计为一个可扩展的插件系统,允许用户根据需要动态加载不同城市的地铁数据。
我们在数据获取模块中引入了城市参数,以便在请求地铁数据时指定城市,通过城市请求相对应的地铁数据,从而实现对不同城市地铁数据的灵活支持。
同时,我们在用户界面模块中引入了城市选择功能,允许用户在不同城市之间切换,从而获取相应城市的地铁线路和站点信息。我们还优化了界面的布局和交互逻辑,以提升用户体验。
项目的反思
在项目的后期开发中,我们发现了一些潜在的问题和改进的空间。如:
- 在路径规划算法中,我们使用广度优先搜索(BFS)算法进行路径搜索,但在某些复杂情况下,可能会导致搜索效率低下。未来可以考虑引入其他算法,如 A* 搜索算法,以提高路径规划的效率。
- 由于缺少资料,我们没有在其他城市中支持票价计算功能。
- 由于对 PyQt5 的不了解,我们在界面设计上遇到了一些困难,也尚未支持线路图示的功能。未来可以考虑进行更多的学习和研究,以提升界面的美观性和易用性。
参见
部分源代码
路径规划算法
| |
构建站点对象
| |
获取信息
| |
主程序
| |